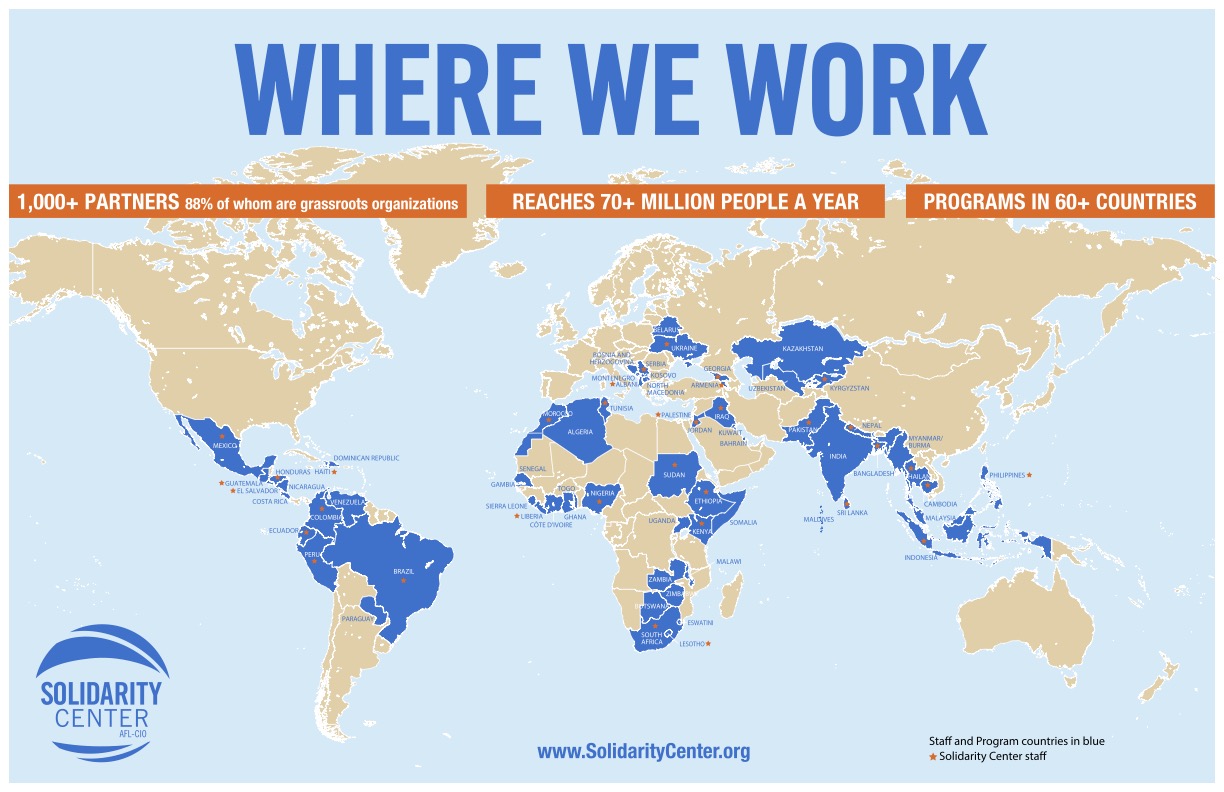
No other organization matches the breadth and depth of the Solidarity Center’s work
The Solidarity Center is a leading international, U.S.-based nonprofit organization dedicated to advancing global worker rights. As a critical force in the global labor movement, our programs are instrumental in fostering fair economies and vibrant democracies.
Our work
Programs in
Countries
Reach:
MILLION
Partners with
88 PERCENT OF WHOM ARE GRASSROOTS ORGANIZATIONS